There is a lot of confusion about the difference between entrepreneurship and intrapreneurship or what is entrepreneurship vs intrapreneurship. This article will clear up all the confusion regarding entrepreneurship and Intrapreneurship. Intrapreneurship is often seen as an opportunity to start your own business without risk. But there are many differences between these two concepts. So, let’s explore together what these terms are and what are major differences between the two.
Who is an Entrepreneur?

An entrepreneur is a person who starts his business from scratch.A business can be based on an original idea, something so unique that it competes in a blue ocean – a market space unrivalled by competitors. Or it could be an iteration of an existing idea or concept, a new product coming into fierce competition in a red ocean market.
Entrepreneurship is the inherent risk that a founder takes when starting their business.
When all goes according to plan, entrepreneurs are often handsomely rewarded for their efforts at the top of the pyramid of a large successful organisation.
On the other hand, if the business fails, entrepreneurs take all the risk and can end up in debt.
Some Inspiring Entrepreneurs Are:
- Professor Yunus (social impact)
- Oprah (media)
- Steve Jobs (tech)
- Giorgio Armani (fashion)
- Brian Chesky (sharing economy/accommodation)
Who is an Intrapreneur?
An Intrapreneur or an insider is an employee responsible for innovative changes in an existing business. Sort of an entrepreneur within a company. They are usually assigned projects that significantly impact the company’s future success and have full access to all available resources, funding, and personnel.
The biggest difference between an insider and an entrepreneur is, of course, risk. The organisation for which the intrapreneur works covers all related costs and possible consequences, while the intrapreneur himself would take the hit.
Some famous intrapreneurs are:
- Ken Kutaragi (creator of PlayStation at Sony)
- Brothers Lars and Jens Eilstrup Rasmussen (creators of Google Maps)
- Paul Buchheit,(the creator of Gmail)
Common Facts Between Entrepreneurship and Intrapreneurship?
Entrepreneurship vs Intrapreneurship is understood through above mentioned details, but now let us look at the similarities between them. There is a lot of overlap between entrepreneurship and intrapreneurship – especially in entrepreneurial thinking.
Both have to lead change and innovate within their organisations (albeit in very different circumstances), which means many commonalities.
Stubbornness In Entrepreneurship and Intrapreneurship?
Both intrapreneurs and entrepreneurs must be stubborn about their decisions. Starting a new company or removing obstacles to digital transformation in an organisation is not easy. Most people are naturally resistant to change. Hence, they both must build a strong will to stay with their decisions and fulfil them.
Leadership Qualities In Intrapreneurs and Entrepreneurs
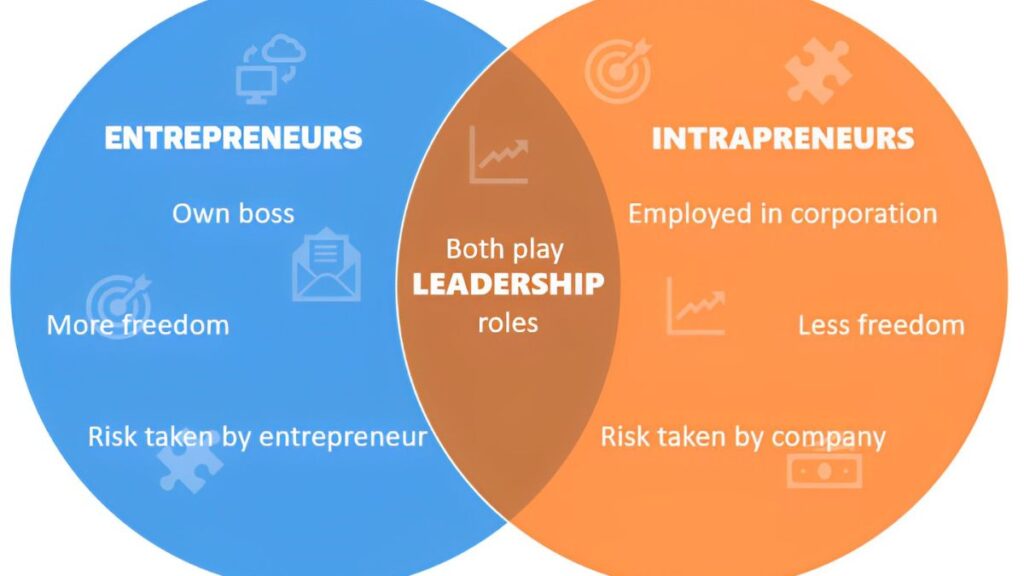
The idea or project may be of a single person, but it takes the combined efforts of a dedicated team to make it successful. This applies to both intrapreneurs and entrepreneurs. That’s why leadership skills are crucial.
Other than this, entrepreneurs and intrapreneurs must also have adaptable nature so they can make quick decisions per the required situation. Also, they both have to be innovative and creative, which helps them to bring something out of the box.
Difference Between Entrepreneurship and Intrapreneurship
These are some key differences between entrepreneurship and Intrapreneurship:
- An entrepreneur starts his own business or works while intrapreneurs work for an existing company.
- Risk: Entrepreneurship is considered riskier than Intrapreneurship because there is no guarantee that the new business will succeed. At the same time, in-house has less chance because it takes place in an existing business.
- Skills: Entrepreneurship requires different skills than Intrapreneurship – for example, an entrepreneur needs to think strategically about how to build their business from scratch. In contrast, an intrapreneur may only need basic management skills.
- Resources: An entrepreneur uses his resources to succeed in his ideas, while an intrapreneur uses the resources provided by the respective company or organisation to implement an idea or plan.
- Capital: Entrepreneurs raise their money themselves, while the company finances Intrapreneurs.
- Work: Entrepreneurs work to develop their market and create a leading position among other starters. On the other hand, Intrapreneurs put their efforts into changing and renewing the existing part of an organisation or company into a better one.
- The core objective of Intrapreneurship is to increase the competitive strength and market sustainability of the organisation, while entrepreneurship focuses on innovating something new of socioeconomic value.
Finally, it’s important to remember that entrepreneurship and in-house operations are not mutually exclusive—many successful entrepreneurs started as in-house entrepreneurs before branching out.
Conclusion
However, it is useful to understand the key differences between entrepreneurship and intrapreneurship when deciding which may be right for you. If you’re trying to decide whether you want to be an entrepreneur or an intrapreneur, both roles have their advantages.
If you are good at networking, can solve problems, and have time for business, you may be interested in being an entrepreneur. This role should allow you to create any product or company you can think of. However, you must know much about the market you want to enter to become an entrepreneur.
For more insights and ideas related to businesses, marketing, social media, financial awareness, business essentials and technology check out BiznessHub, to explore further opportunities and knowledge.
FAQs
Ques. Who is an entrepreneur?
Ans. Entrepreneurs are those who start their own businesses with unique ideas or concepts.
Ques. Who is Intrapreneur?
Ans. Intrapreneur represents the employee of the organisation who carries a unique idea/concept within the organisational boundaries.
Ques. What are the benefits of becoming an intrapreneur?
Ans. Intrapreneurs have the ability to earn a good amount, become self-independent, lead a team, learn team-building skills, management skills, and many more.




